DOM操作CSS
通过JS修改元素的样式
语法:
- 元素.style.样式名 = 样式值
注意:
- 如果CSS的样式名中含有:
- 这种名称在JS中是不合法的比如background-color
- 需要将这种样式名修改为驼峰命名法
- 去掉-,然后将-后的字母大写,如
backgroundColor- 我们通过style属性设置的样式都是内联样式,而内联样式有较高的优先级,所以通过JS修改的样式往往会立即显示
- 但是如果在样式中写了!important,则此时样式会有最高的优先级,即使通过JS也不能覆盖该样式,此时将会导致JS修改样式失效
通过JS读取元素的样式
style
语法:
- 元素.style.样式名
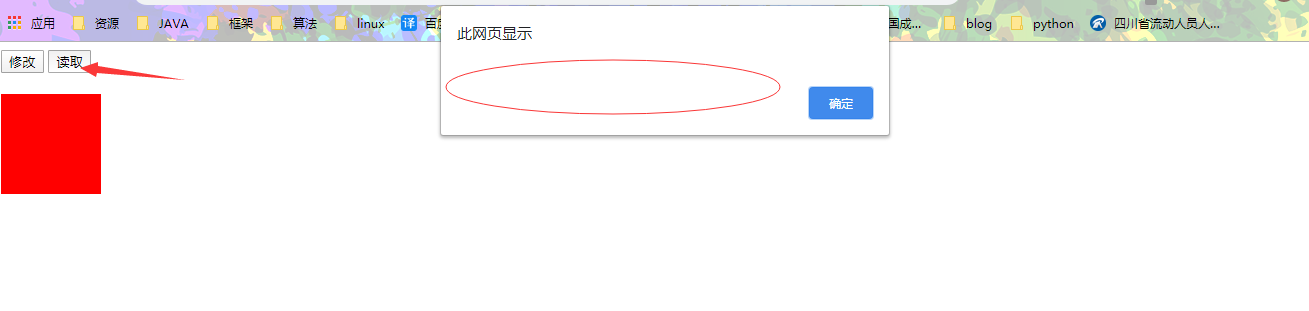
通过style属性设置和读取的都是内联样式,无法读取样式表中的样式
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
//获取box1
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
//为按钮绑定单击响应函数
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
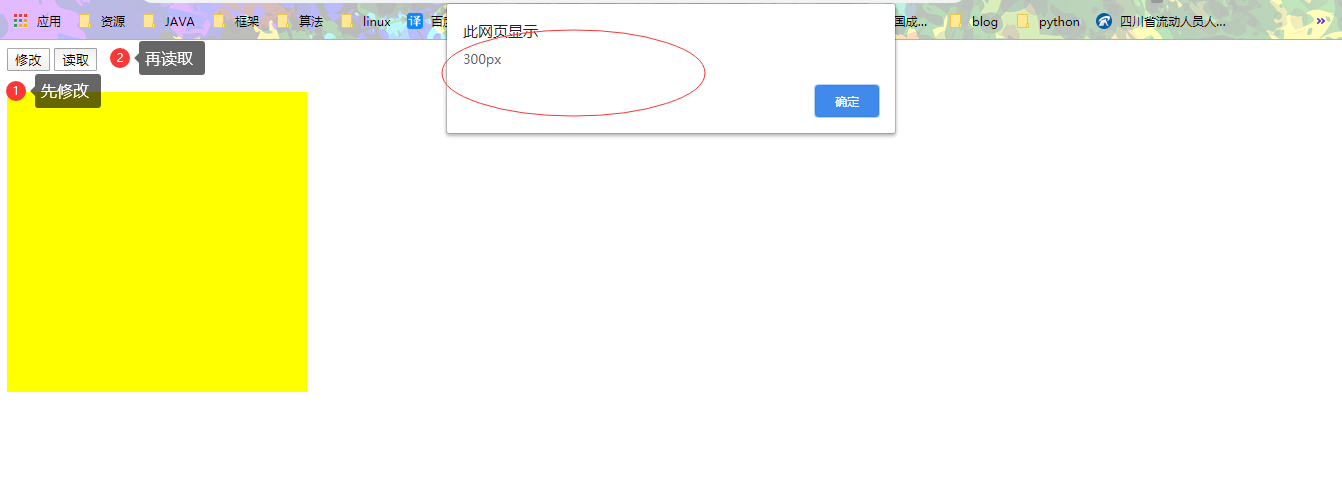
btn01.onclick = function(){
box1.style.width = "300px";
box1.style.height = "300px";
box1.style.backgroundColor = "yellow";
};
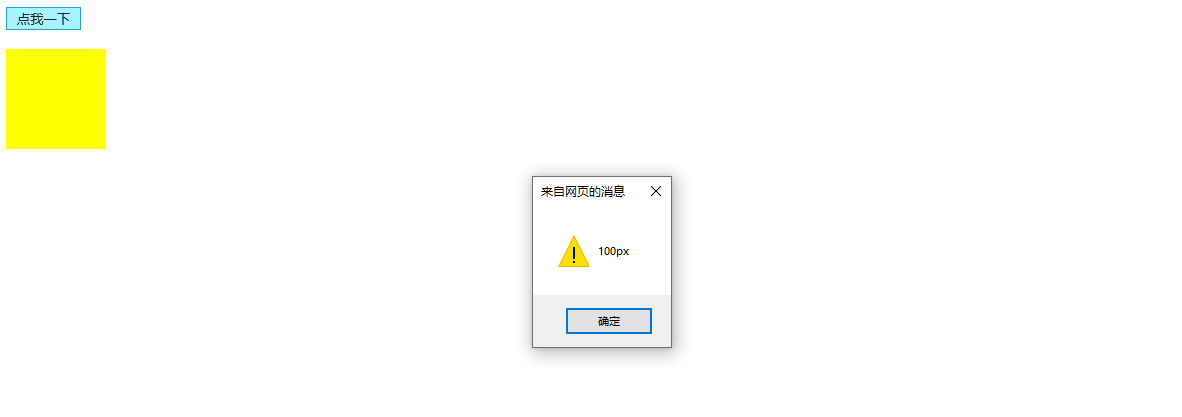
//点击按钮2以后,读取元素的样式
var btn02 = document.getElementById("btn02");
btn02.onclick = function(){
//alert(box1.style.height);
alert(box1.style.width);
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<button id="btn02">点我一下2</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>
可以发现,直接点击读取,是无法读取到样式表里的样式属性值的,而通过第一个按钮,修改了内联样式之后,在读取,即可读取到元素的属性值
currentStyle
获取元素的当前显示的样式,
currentStyle只有IE浏览器支持,其他的浏览器都不支持语法:
- 元素.currentStyle.样式名
- 它可以用来读取当前元素正在显示的样式
如果当前元素没有设置该样式,则获取它的默认值
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
//点击按钮以后读取box1的样式
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
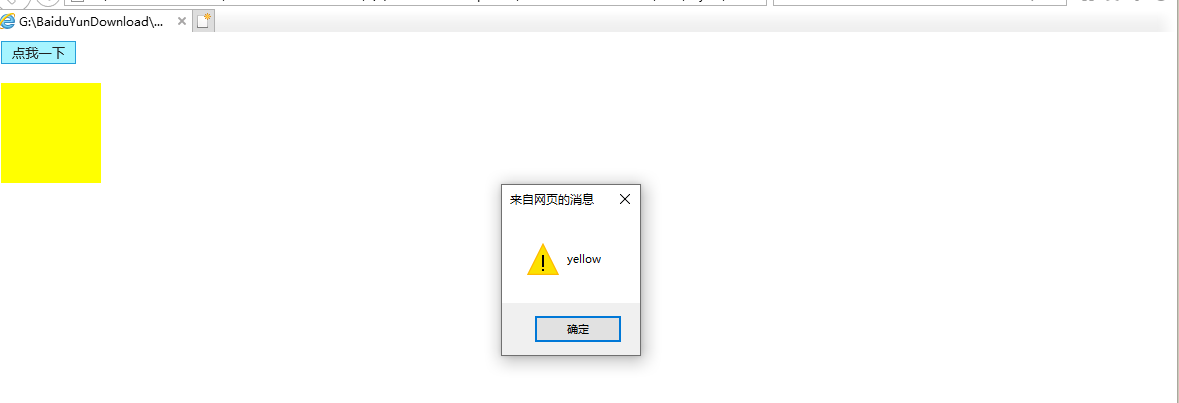
btn01.onclick = function(){
//在此之前是没有设置内联样式的,currentStyle可以获取样式表里的样式
alert(box1.currentStyle.backgroundColor);
};
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box1" ></div>
</body>
</html>
getComputedStyle()
在其他浏览器中可以使用,
getComputedStyle()这个方法来获取元素当前的样式,这个方法是window的方法,可以直接使用。但是该方法不支持IE8及以下的浏览器需要两个参数:
- 第一个:要获取样式的元素
- 第二个:可以传递一个伪元素,一般都传null
该方法会返回一个对象,对象中封装了当前元素对应的样式
- 读取样式可以通过
- 对象.样式名
如果获取的样式没有设置,则会获取到真实的值,而不是默认值
- 比如:没有设置width,它不会获取到auto,而是一个长度
- 通过
currentStyle和getComputedStyle()读取到的样式都是只读的,不能修改,如果要修改必须通过style属性
获取样式解决浏览器兼容
自定义getStyle()
用来解决浏览器兼容性问题,做了一个适配性的自定义函数
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
//点击按钮以后读取box1的样式
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
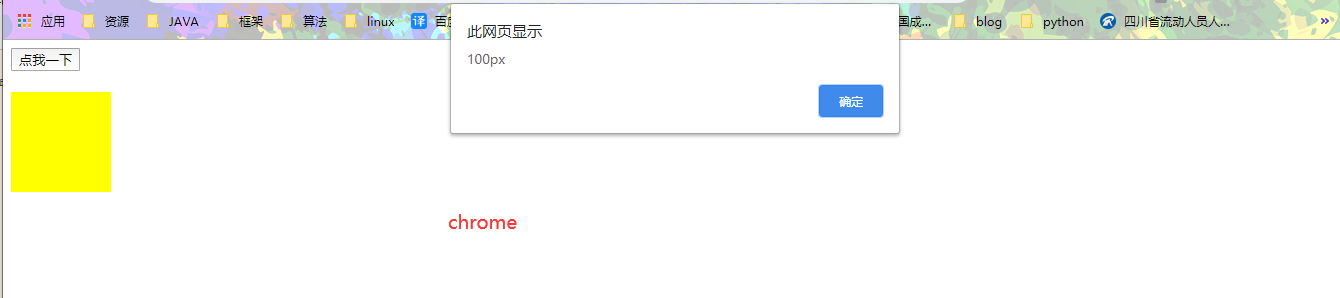
btn01.onclick = function(){
alert(getStyle(box1,"width"));
};
};
/*
* 定义一个函数,用来获取指定元素的当前的样式
* 参数:
* obj 要获取样式的元素
* name 要获取的样式名
*/
function getStyle(obj , name){
if(window.getComputedStyle){
//正常浏览器的方式,具有getComputedStyle()方法
return getComputedStyle(obj , null)[name];
}else{
//IE8的方式,没有getComputedStyle()方法
return obj.currentStyle[name];
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box1" ></div>
</body>
</html>
chrome
IE
其他样式操作属性
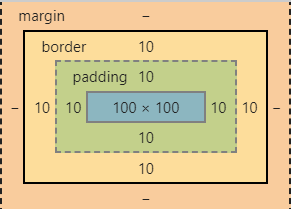
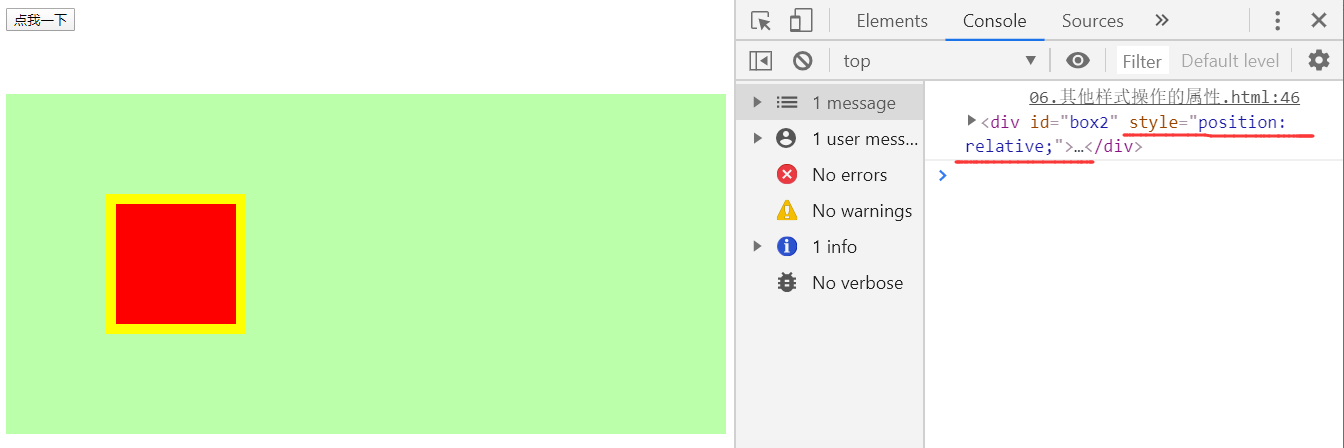
clientWidth与clientHeight
- 这两个属性可以获取元素的可见宽度和高度
- 这些属性都是不带px的,返回都是一个数字,可以直接进行计算
- 会获取元素宽度和高度,包括内容区和内边距
- 这些属性都是只读的,不能修改
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
padding: 10px;
border: 10px solid yellow;
}
#box2{
padding: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
btn01.onclick = function(){
console.log(box1.clientWidth);
console.log(box1.clientHeight);
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body id="body">
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box3">
<div id="box2" style="position: relative;">
<div id="box1"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
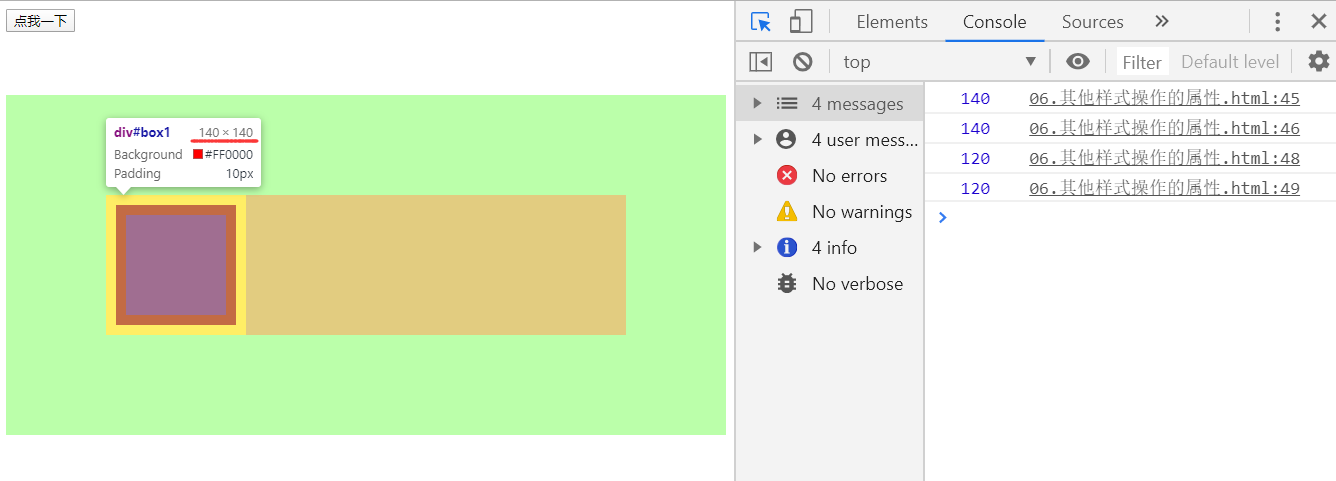
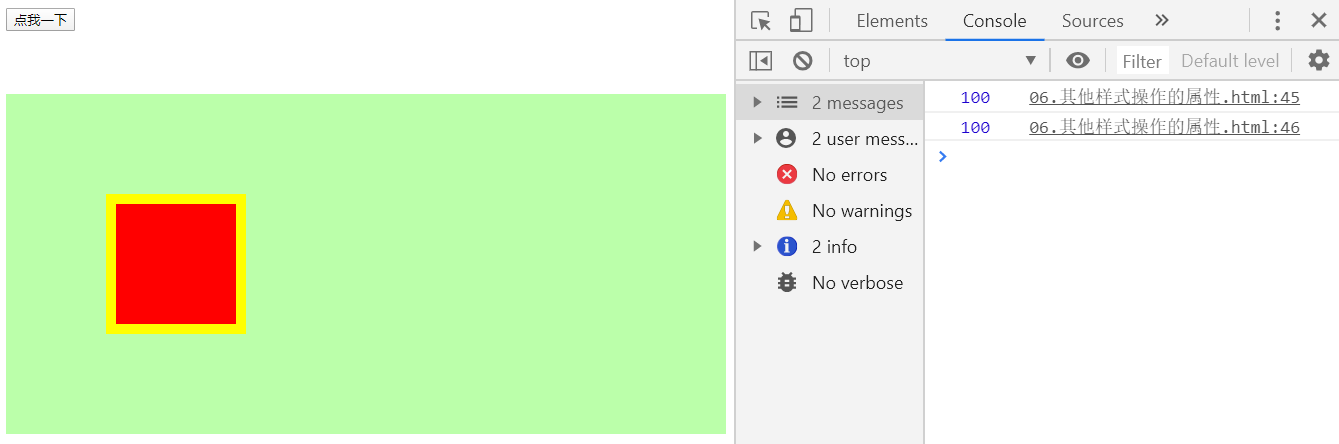
offsetWidth与offsetHeight
- 获取元素的整个的宽度和高度,包括内容区、内边距和边框
- 因此与
clientWidth与clientHeight的区别就是没有算入边框大小
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
padding: 10px;
border: 10px solid yellow;
}
#box2{
padding: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
btn01.onclick = function(){
console.log(box1.offsetWidth);
console.log(box1.offsetHeight);
//clientWidth对比
console.log(box1.clientWidth);
console.log(box1.clientHeight);
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body id="body">
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box3">
<div id="box2" style="position: relative;">
<div id="box1"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
offsetParent
- 可以用来获取当前元素的定位父元素
- 会获取到离当前元素最近的开启了定位的祖先元素
- 如果所有的祖先元素都没有开启定位,则返回body
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
padding: 10px;
border: 10px solid yellow;
}
#box2{
padding: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
btn01.onclick = function(){
var op = box1.offsetParent;
console.log(op);
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body id="body">
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box3">
<div id="box2" style="position: relative;">
<div id="box1"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
如果取消了box2的定位的话,则返回的是body
offsetLeft与offsetTop
offsetLeft
- 当前元素相对于其定位父元素的水平偏移量
offsetTop
- 当前元素相对于其定位父元素的垂直偏移量
注意:
- 必须相对于定位的父元素,找父元素类同与
offsetParent
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
padding: 10px;
border: 10px solid yellow;
}
#box2{
padding: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
btn01.onclick = function(){
/*
* offsetLeft
* - 当前元素相对于其定位父元素的水平偏移量
* offsetTop
* - 当前元素相对于其定位父元素的垂直偏移量
*/
console.log(box1.offsetLeft);
console.log(box1.offsetTop);
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body id="body">
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box3">
<div id="box2" style="position: relative;">
<div id="box1"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
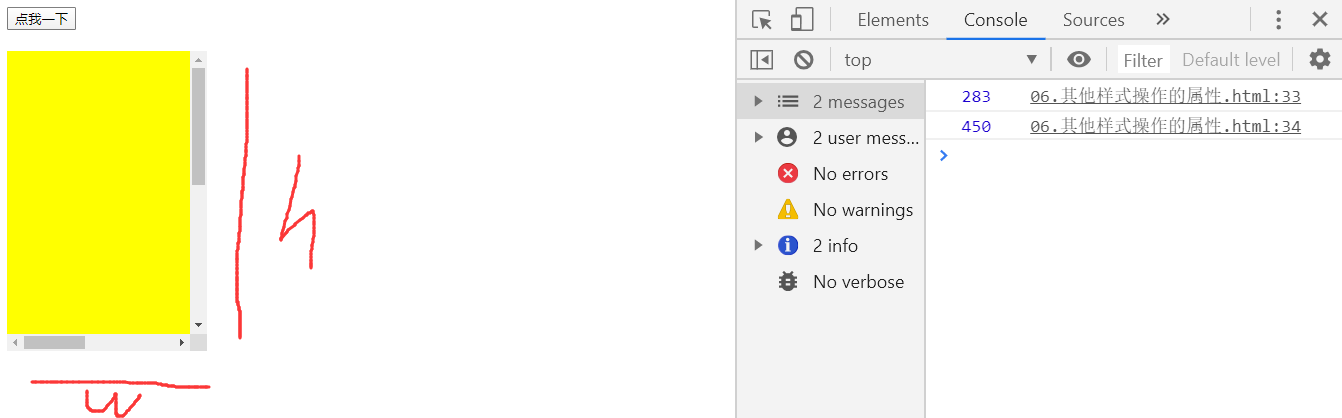
scrollWidth与scrollHeight
可以获取元素整个滚动区域的宽度和高度
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #bfa;
overflow: auto;
}
#box2{
width: 450px;
height: 600px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
btn01.onclick = function(){
console.log(box1.clientHeight);
console.log(box1.scrollWidth);
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body id="body">
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box1">
<div id="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
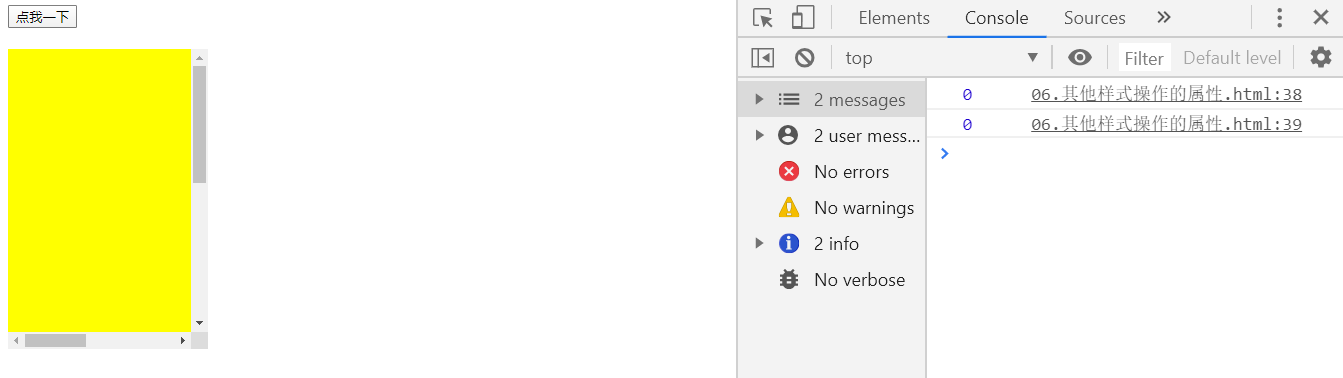
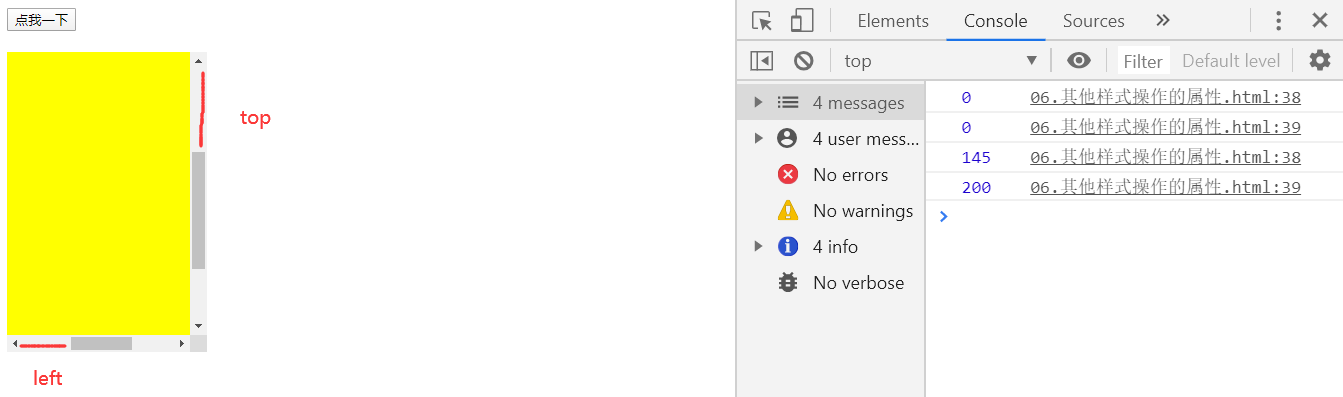
scrollLeft与scrollTop
scrollLeft
- 可以获取水平滚动条滚动的距离
scrollTop
- 可以获取垂直滚动条滚动的距离
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #bfa;
overflow: auto;
}
#box2{
width: 450px;
height: 600px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
btn01.onclick = function(){
console.log(box1.scrollLeft);
console.log(box1.scrollTop);
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body id="body">
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box1">
<div id="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
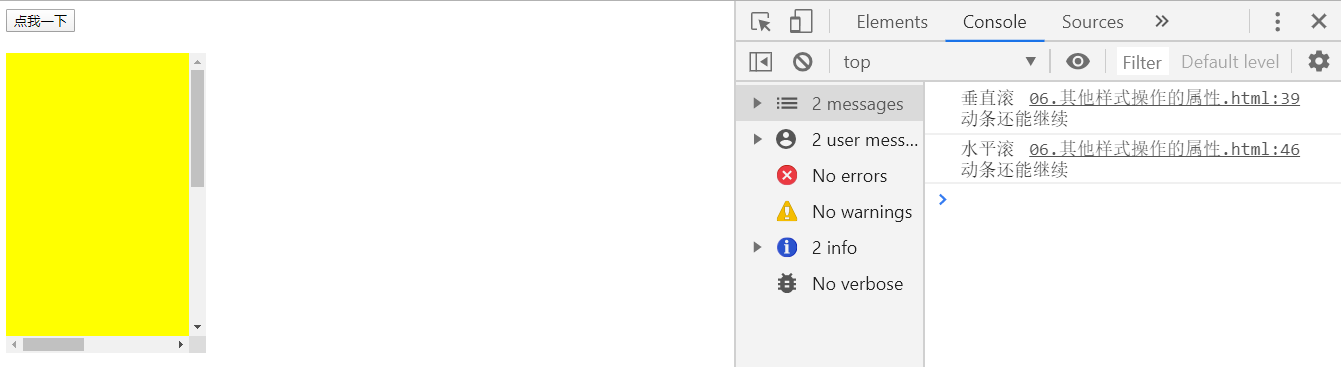
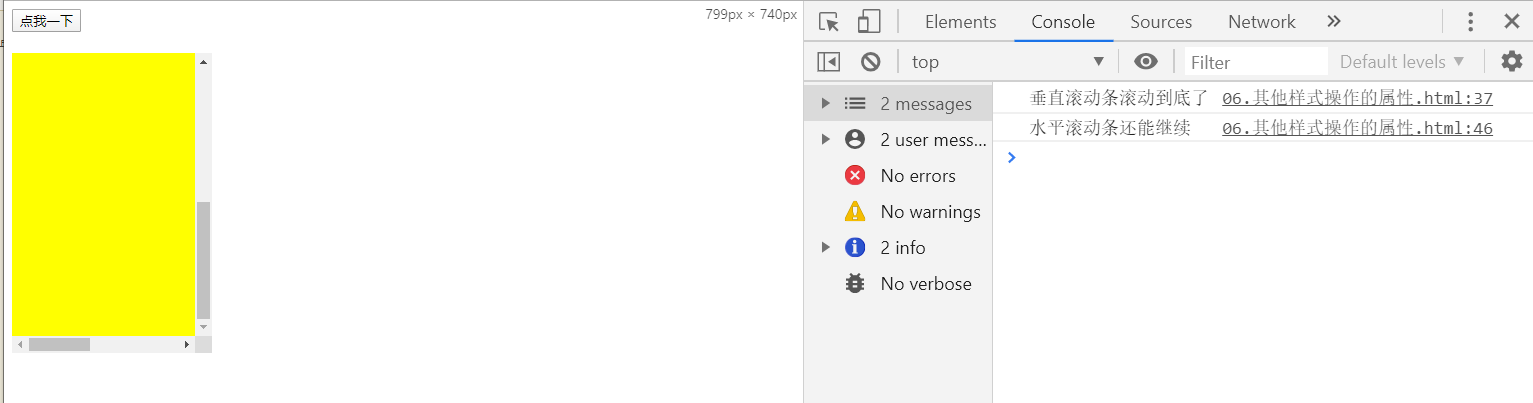
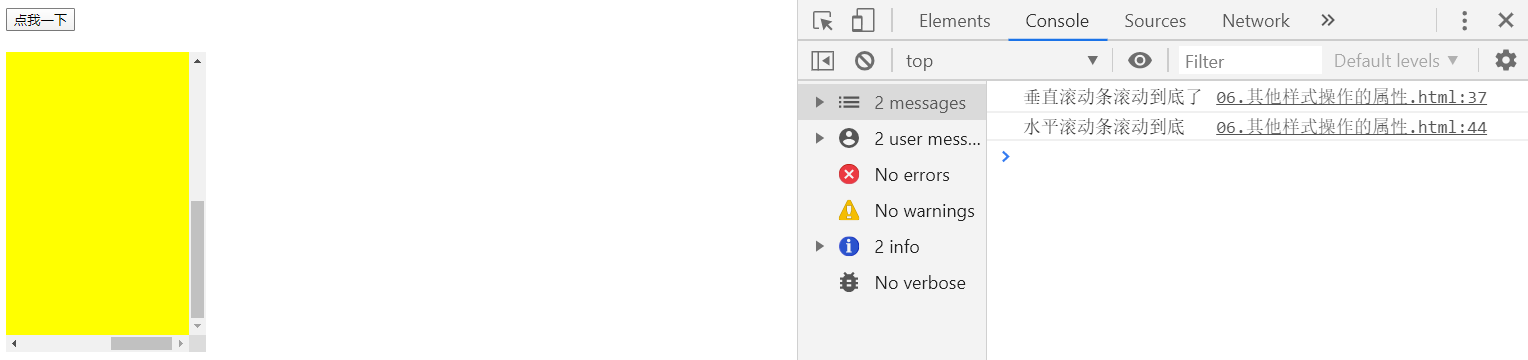
判断滚动条是否滑到底
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#box1{
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #bfa;
overflow: auto;
}
#box2{
width: 450px;
height: 600px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var btn01 = document.getElementById("btn01");
var box1 = document.getElementById("box1");
btn01.onclick = function(){
//滚动条实际长度 - 滑动长度 == 0 即为到底
//当满足scrollHeight - scrollTop == clientHeight
//说明垂直滚动条滚动到底了
if(box1.scrollHeight - box1.scrollTop == box1.clientHeight)
console.log("垂直滚动条滚动到底了");
else
console.log("垂直滚动条还能继续");
//当满足scrollWidth - scrollLeft == clientWidth
//说明水平滚动条滚动到底
if(box1.scrollWidth - box1.scrollLeft == box1.clientWidth)
console.log("水平滚动条滚动到底");
else
console.log("水平滚动条还能继续");
};
};
</script>
</head>
<body id="body">
<button id="btn01">点我一下</button>
<br /><br />
<div id="box1">
<div id="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>